运行时重启SpringBoot Application
需求背景
在一个很奇葩的需求下,要求在客户端动态修改Spring Boot配置文件中的属性,例如端口号、应用名称、数据库连接信息等,然后通过一个Http请求重启Spring Boot程序。这个需求类似于操作系统更新配置后需要进行重启系统才能生效的应用场景。
动态配置系统并更新生效是应用的一种通用性需求,实现的方式也有很多种。例如监听配置文件变化、使用配置中心等等。网络上也有很多类似的教程存在,但大多数都是在开发阶段,借助Spring Boot DevTools插件实现应用程序的重启,或者是使用spring-boot-starter-actuator和spring-cloud-starter-config来提供端点(Endpoint)的刷新。
第一种方式无法在生产环境中使用(不考虑),第二种方式需要引入Spring Cloud相关内容,这无疑是杀鸡用了宰牛刀。
接下来,我将尝试采用另外一种方式实现HTTP请求重启Spring Boot应用程序这个怪异的需求。
尝试思路
重启Spring Boot应用程序的关键步骤是对主类中**SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);方法返回值的处理。SpringApplication#run()方法将会返回一个ConfigurableApplicationContext类型对象,通过查看官方文档可以看到,ConfigurableApplicationContext接口类中定义了一个close()**方法,可以用来关闭当前应用的上下文:
package org.springframework.context;
import java.io.Closeable;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.io.ProtocolResolver;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable {
void close();
}
继续看官方源码,AbstractApplicationContext类中实现**close()**方法,下面是实现类中的方法摘要:
public void close() {
Object var1 = this.startupShutdownMonitor;
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
this.doClose();
if (this.shutdownHook != null) {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);
} catch (IllegalStateException var4) {
;
}
}
}
}
**#close()方法将会调用#doClose()方法,我们再来看看#doClose()方法做了哪些操作,下面是doClose()**方法的摘要:
protected void doClose() {
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
...
LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this);
...
this.destroyBeans();
this.closeBeanFactory();
this.onClose();
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners != null) {
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
this.active.set(false);
}
}
在**#doClose()**方法中,首先将应用上下文从注册表中清除掉,然后是销毁Bean工厂中的Beans,紧接着关闭Bean工厂。
官方文档看到这里,就产生了解决一个结局重启应用应用程序的大胆猜想。在应用程序的main()方法中,我们可以使用一个临时变量来存放SpringApplication.run()返回的ConfigurableApplicationContext对象,当我们完成对Spring Boot应用程序中属性的设置后,调用ConfigurableApplicationContext的**#close()**方法,最后再调用SpringApplication.run()方法重新给ConfigurableApplicationContext对象进行赋值已达到重启的效果。
现在,我们再来看一下SpringApplication.run()方法中是如何重新创建ConfigurableApplicationContext对象的。在SpringApplication类中,run()方法会调用createApplicationContext()方法来创建一个ApplicationContext对象:
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch(this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext");
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext");
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", var3);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
createApplicationContext()方法会根据WebApplicationType类型来创建ApplicationContext对象。在WebApplicationType中定义了三种种类型:NONE、SERVLET和REACTIVE。通常情况下,将会创建servlet类型的ApplicationContext对象。
接下来,我将以一个简单的Spring Boot工程来验证上述的猜想是否能够达到重启Spring Boot应用程序的需求。
编码实现
首先,在application.properties文件中加入如下的配置信息,为动态修改配置信息提供数据:
spring.application.name= SPRING-BOOT-APPLICATION
接下来,在Spring Boot主类中定义两个私有变量,用于存放main()方法的参数和SpringApplication.run()方法返回的值。下面的代码给出了主类的示例:
public class ExampleRestartApplication {
@Value ( "${spring.application.name}" )
String appName;
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger ( ExampleRestartApplication.class );
private static String[] args;
private static ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExampleRestartApplication.args = args;
ExampleRestartApplication.context = SpringApplication.run(ExampleRestartApplication.class, args);
}
}
最后,直接在主类中定义用于刷新并重启Spring Boot应用程序的端点(Endpoint),并使用**@RestController**注解对主类进行注释。
@GetMapping("/refresh")
public String restart(){
logger.info ( "spring.application.name:"+appName);
try {
PropUtil.init ().write ( "spring.application.name","SPRING-DYNAMIC-SERVER" );
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace ( );
}
ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor (1,1,0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<> ( 1 ),new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy ());
threadPool.execute (()->{
context.close ();
context = SpringApplication.run ( ExampleRestartApplication.class,args );
} );
threadPool.shutdown ();
return "spring.application.name:"+appName;
}
说明:为了能够重新启动Spring Boot应用程序,需要将close()和run()方法放在一个独立的线程中执行。
为了验证Spring Boot应用程序在被修改重启有相关的属性有没有生效,再添加一个获取属性信息的端点,返回配置属性的信息。
@GetMapping("/info")
public String info(){
logger.info ( "spring.application.name:"+appName);
return appName;
}
完整的代码
下面给出了主类的全部代码:
package com.ramostear.application;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @author ramostear
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class ExampleRestartApplication {
@Value ( "${spring.application.name}" )
String appName;
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger ( ExampleRestartApplication.class );
private static String[] args;
private static ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExampleRestartApplication.args = args;
ExampleRestartApplication.context = SpringApplication.run(ExampleRestartApplication.class, args);
}
@GetMapping("/refresh")
public String restart(){
logger.info ( "spring.application.name:"+appName);
try {
PropUtil.init ().write ( "spring.application.name","SPRING-DYNAMIC-SERVER" );
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace ( );
}
ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor (1,1,0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<> ( 1 ),new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy ());
threadPool.execute (()->{
context.close ();
context = SpringApplication.run ( ExampleRestartApplication.class,args );
} );
threadPool.shutdown ();
return "spring.application.name:"+appName;
}
@GetMapping("/info")
public String info(){
logger.info ( "spring.application.name:"+appName);
return appName;
}
}
接下来,运行Spring Boot程序,下面是应用程序启动成功后控制台输出的日志信息:
[2019-03-12T19:05:53.053z][org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ExecutorConfigurationSupport][main][171][INFO ] Initializing ExecutorService 'applicationTaskExecutor'
[2019-03-12T19:05:53.053z][org.apache.juli.logging.DirectJDKLog][main][173][INFO ] Starting ProtocolHandler ["http-nio-8080"]
[2019-03-12T19:05:53.053z][org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer][main][204][INFO ] Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
[2019-03-12T19:05:53.053z][org.springframework.boot.StartupInfoLogger][main][59][INFO ] Started ExampleRestartApplication in 1.587 seconds (JVM running for 2.058)
在测试修改系统配置并重启之前,使用Postman测试工具访问:http://localhost:8080/info ,查看一下返回的信息:
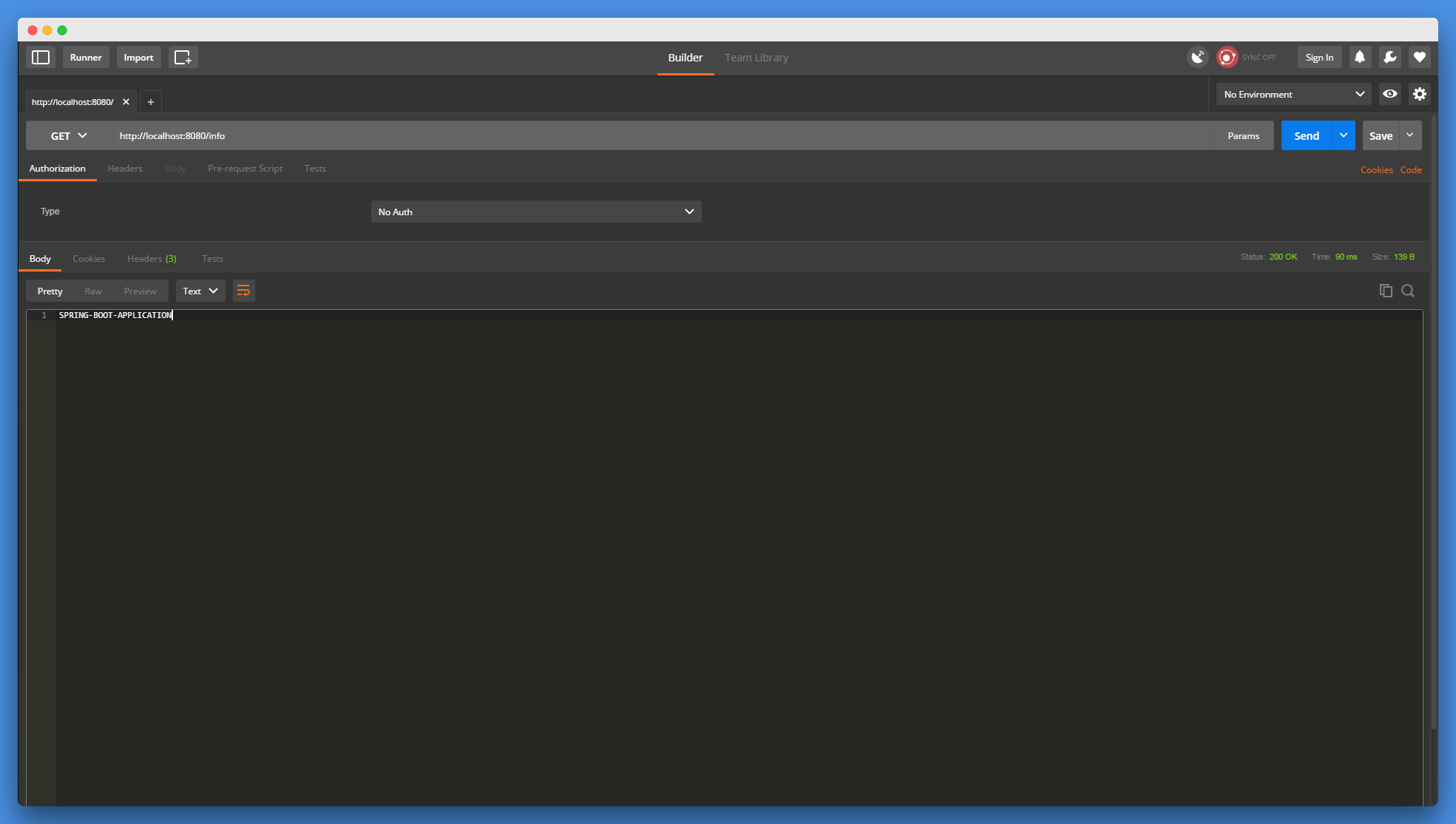
成功返回SPRING-BOOT-APPLICATION提示信息。
然后,访问:http://localhost:8080/refresh ,设置应用应用程序spring.application.name的值为SPRING-DYNAMIC-SERVER,观察控制台输出的日志信息:
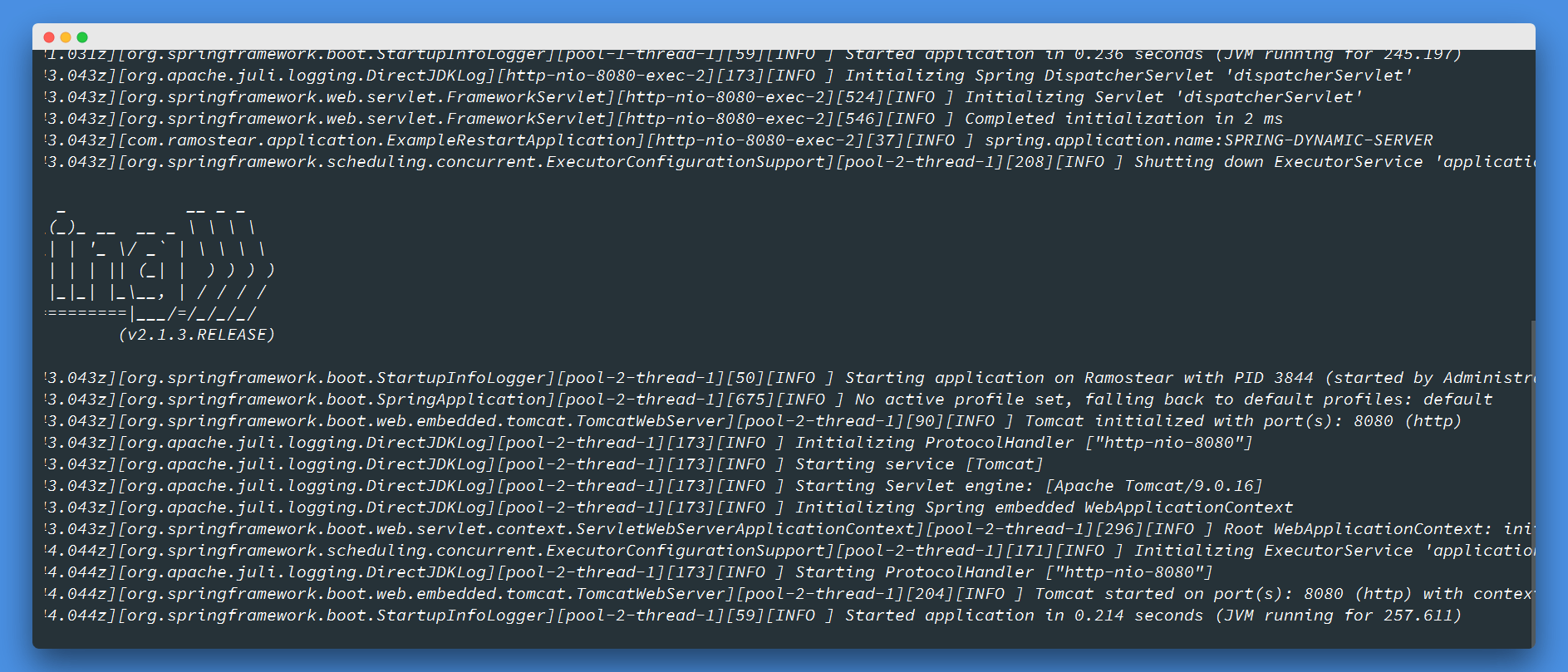
可以看到,Spring Boot应用程序已经重新启动成功,最后,在此访问:http://localhost:8080/info ,验证之前的修改是否生效:
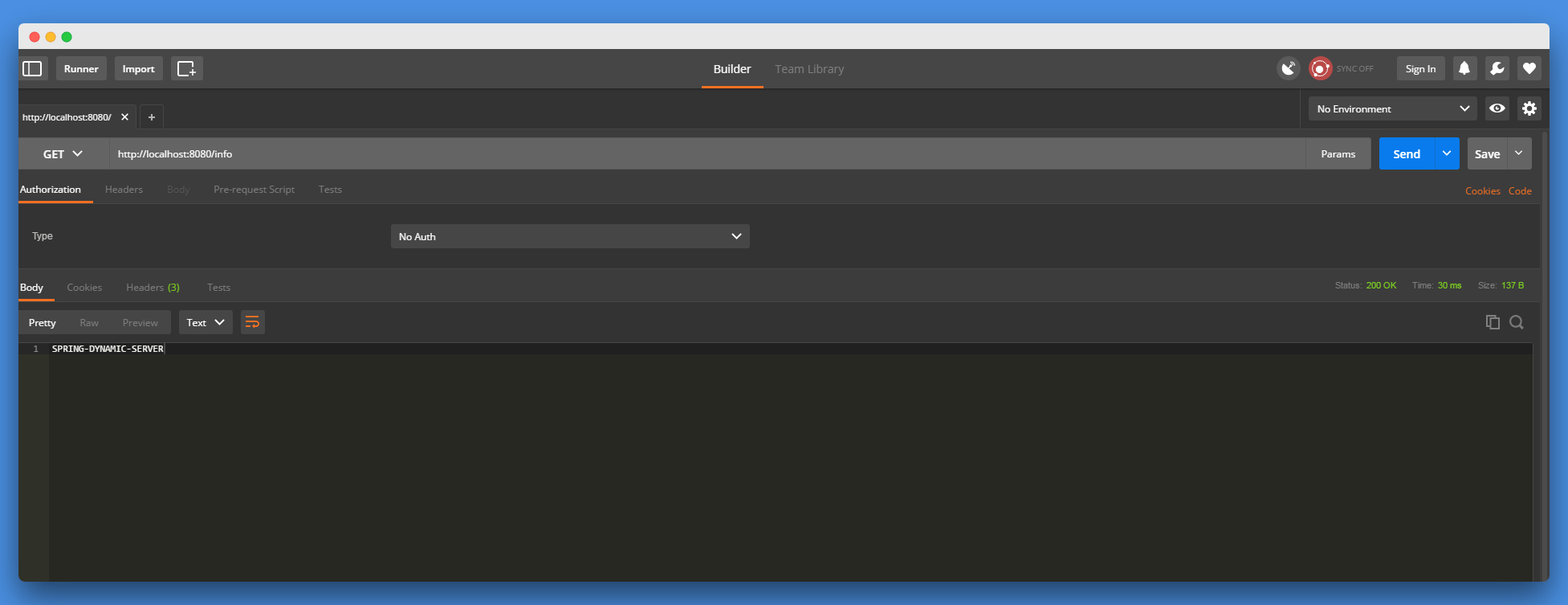
请求成功返回了SPRING-DYNAMIC-SERVER信息,最后在看一眼application.properties文件中的配置信息是否真的被修改了:
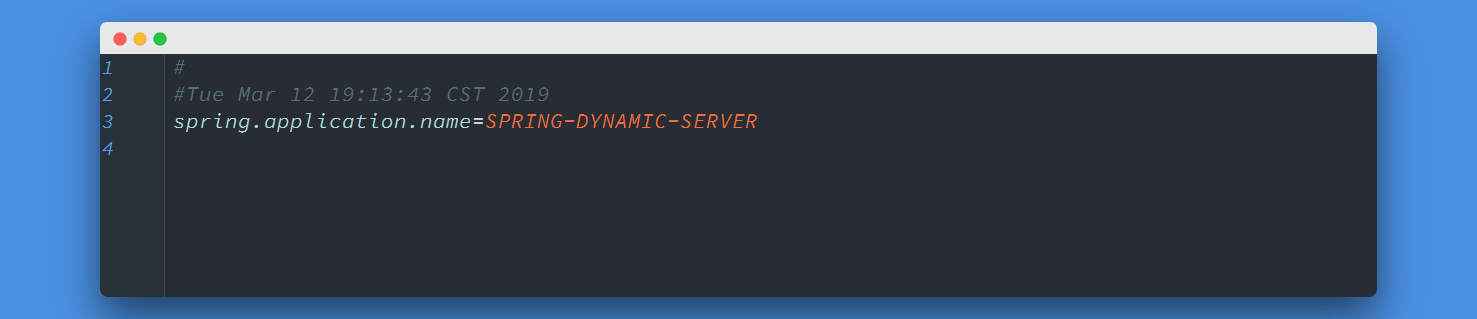
配置文件的属性也被成功的修改,证明之前的猜想验证成功了。
本次内容所描述的方法不适用于以JAR文件启动的Spring Boot应用程序,以WAR包的方式启动应用程序亲测可用。┏ (ω)=☞目前该药方副作用未知,如有大牛路过,还望留步指点迷津,不胜感激。
结束语
本次内容记录了自己验证HTTP请求重启Spring Boot应用程序试验的一次经历,文章中所涉及到的内容仅代表个人的一些观点和不成熟的想法,并未将此方法应用到实际的项目中去,如因引用本次内容中的方法应用到实际生产开发工作中所带来的风险,需引用者自行承担因风险带来的后遗症(๑→ܫ←)——此药方还有待商榷(O_o)(o_O)。




评论区